It doesn’t really matter how much you study it, it’s almost impossible to get the perfect SEO (Search Engine Optimization) score for any long period of time. Each search engine has their own algorithm to rank web sites, and as if that wasn’t complicated enough, they change that algorithm frequently in order to perfect it and make sure that the same sites doesn’t hog up the top positions simply because they’ve figured out the x-factor in the algorithm to dodge other more popular sites that have the traffic, content mass, and extensive Internet presence enough to be ranked at the top.
There are of course some key pillars that one should make sure to implement that seemingly every search engine incorporates. SEO is your website’s conversation with search engines. Through tools like link building, quality content, apt tags, keywords, etc., search engines navigate through your website.
Purpose?
To up your website’s ranking, impacting traffic and lead generation. Bad SEO, aka black hat, violates googles terms by using unethical practices or dubious tactics and poor implementation.
Result?
Poor traffic, missed opportunities, bad user experience, wastage of time and effort, and eventually, long-term damage to your website.
In this article, we list down some practices you should avoid for better SEO practices.
Here is the List of 10 Bad Practices To Avoid While Doing SEO:
1. Having Thin Content on Your Webpages
Google describes it as poor quality, shallow, duplicative content, adding no value to the user. Content is essential for both inbound marketing and SEO. Search engines get to know what the page is about through content (texts, images, videos, infographics). Content will help you generate traffic, grow inbound links, and enhance social media engagement, thus, setting a strong foundation.
Some useful data-
I. 72% of marketers said content increased engagement and 72% more lead generation for their business.
II. According to the demand metric, content-centric inbound marketing strategies lead to 3x more leads and cost 62% less.
Type Of Thin Content That Invites Google Penalty:
- Automated Content – Generated automatically, doesn’t make sense to readers.
- Thin Affiliate Web Pages – Content from affiliated brands copied across multiple domains,
- Doorway Web Pages – Pages force users to navigate to another page without offering anything substantial.
- Guest Posts – Low-quality posts from other sources.
2. Overusing Keywords
“We offer the best cycles; if you are looking for the best cycles, come to us”. That’s keyword stuffing for you, intended to improve the ranking for that word.
Keywords help users find what they are looking for and for search engines to understand that a particular page is relevant to the search query.
Overusing keywords is strictly disliked by google to the point that it invites penalties. As officially stated by Google, it leads to a bad user experience and lowered ranking.
Examples of irrelevant and overused keywords –
- Repeated phrases (best cycles example).
- Lists of numbers without any substantial value.
- Invisible words on the page.
- Overstuffing in the website’s HTML code, etc.
- Excessive words in alt tags.
Use LSI, synonyms and related words, and AI writing tools to generate apt keywords for your page.
See how this website has overused its target keywords.

3. Following Dubious Practices Related to Link Building-
Link building is the process of building links to different web pages. It results in website authority and improved SERP ranking.
However, improper linking practices could lead to opposite results, inviting the Google penalty.
For instance, Google might deindex your webpage or even the entire website if found using link farms.
Examples of bad linking practices:
- Using Link Farms, i.e., a group of websites that link to each other to improve website ranking.
- Purchasing backlinks from PBNs.
- Have your webpage’s link on low authority websites.
- Too many links from a few sources.
- Embedding links in anchor text match the keywords you want to rank for.
- Reciprocating links for mutual advantage, as seen in web directories.
Take a look at this link farm:

4. Not Understanding the Target Audience
Your target audience is your potential lead generators. These are the people looking for businesses like yours on search engines.
Defining them means knowing the people behind the keywords, and thus, it can help you build a strong SEO strategy.
What does not knowing your customers could mean?
- Waste of time, money, and effort as you might be generating more traffic, but it won’t help if you are not targeting your right audience.
- It means lost revenue, hitting your business’s interest at the very basic level.
Knowing your people will help you find the right keywords, draft apt content, and share on time and at the right channels.
Go for techniques like:
- Collecting their email and following them up with surveys.
- Using CRM software.
- Accessing the demographic information at the time of purchase.
5. Showcasing Excessive Ads
Placing ads on your website is one way of bringing in additional money. It seems tempting, but excessive Ads could adversely affect your business, i.e., you might even invite a Google penalty.
How do excessive Ads affect you?
- It could add much weight to the site page, dragging down the speed.
- It slows down both users and crawlers navigating through your page. Spiders will have difficulty crawling through the page, affecting the crawl budget and, thus, indexing.
- It leads to a bad user experience. Sometimes users avoid websites showcasing those ad types.
“Excessive ads are not sustainable even though profitable in the short term. It could lower your traffic and profits in the long run”, says Cristian Ward of sandiegoseo.company
Avoid practices like too many ads above the fold, auto-playing audios and videos, interstitials, pop-ups, pagination abuse, etc.
Access Google’s Ad Experience Report to know if you are getting penalized.
6. Not Fixing Technical Issues
Building quality content or going for other right practices won’t help if your page has basic structural or technical problems.
The technical aspect of SEO is the website’s ability to fulfill the requirements of search engines with the aim of improved organic ranking. It comprises elements like crawling, indexing, etc.
Some examples of technical issues are:
- No HTTPS security.
- The site doesn’t have XML site maps.
- Broken links, improper redirects, and URLs.
- Badly configured, missing, or incorrect Robots.txt file.
- Improper configuration of NOINDEX tag.
- Not a user-friendly Mobile experience.
- Not using structured data, etc.
These SEO issues are sometimes overlooked but are important to fix, to boost visibility and ranking.
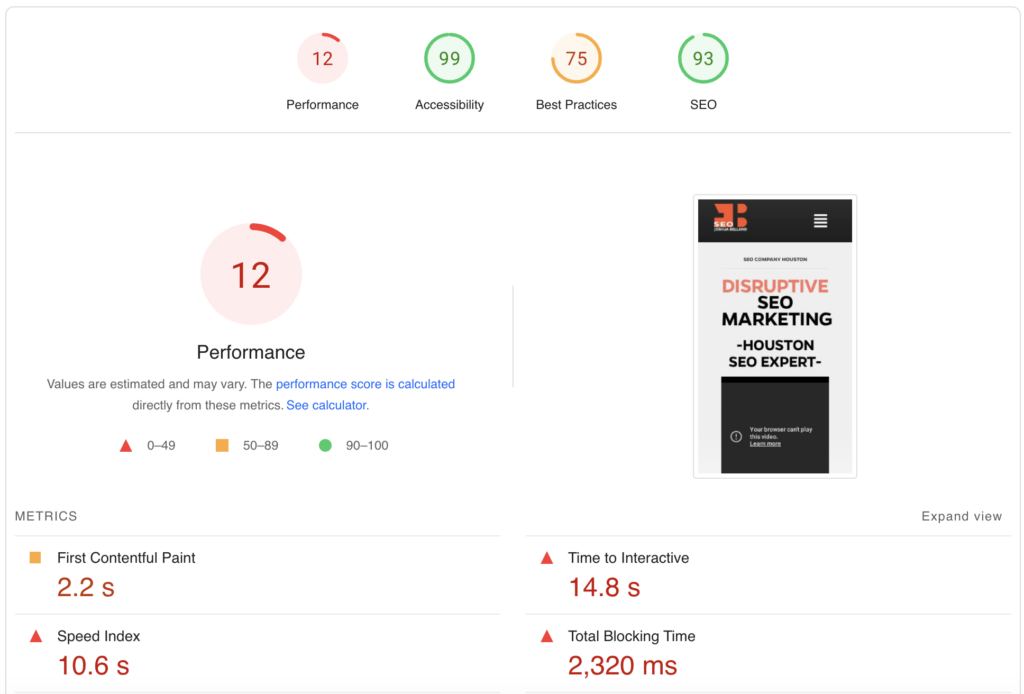
7. Slow Page Loading Speed
Imagine a website that offers great services and apt content but takes ages to load. Would you be willing to wait every time for the page to load?
Unlikely, right?
The ideal time for website download is less than 3-4 seconds, translating to a bad user experience with anything otherwise.
Some useful data:
- Conversions increase by 7% with each lesser second of website loading.
- 53% of the users abandon a page if it takes more than 3 seconds to load.
Result?
I. Bad conversion and lead generation.
II. Bad user experience.
III. It affects traffic and ranking.
IV. Potential customers are gone, affecting your bottom-line growth.
Why does your page load slowly?
- Excessive ADs, Flash Content, HTTPS Requests, etc.
- Images are not optimized.
- Not caching.
- Bad hosting provider.
- Issues with JavaScript.
- Unoptimized CSS (code for styling a website’s pages).
- Images aren’t optimized.
You can measure your page speed on Google PageSpeed Insights.
8. Erratic Content Posting
Posting content here and there is another no-no for good SEO practices. Posting too much content targeting similar keywords will make you compete with your content. It might lead to keyword cannibalization.
Similarly, posting too little will not give search engines the fresh content it needs.
According to a study by HubSpot, marketers who blogged more than 16 times a month generated 3.5x more traffic and 4.5x more leads than those who blogged 0-4 times per month.
How is erratic posting bad for you?
- You don’t upload fresh content for Google.
- It affects the website’s ranking with highly targeted keywords and indexed pages.
- It hampers a website’s ability to build authority with its users steadily.
Things you can do:
I. Try to post one time per day and not more than two.
II. You can try consistently posting 16 times a month for six and a half months to
maximize your content value.
III. Post on a steady basis, diligently.
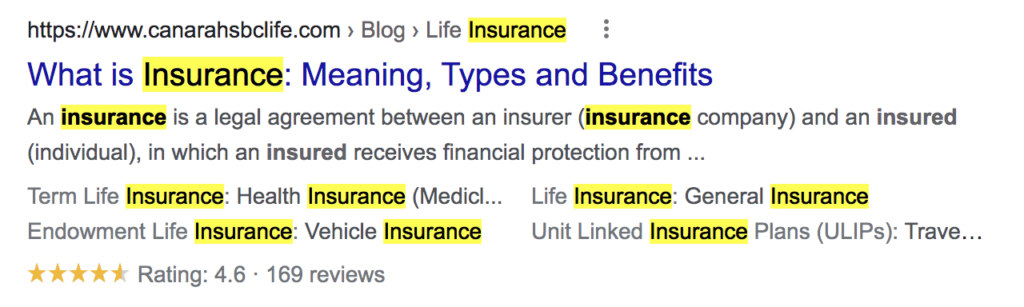
9. Ignoring Meta Information
Meta information is your metadata, i.e., data about your data. It is what lets search engines read your content. So, adding metadata like title, description, keywords, image tags, etc., becomes imperative.
How does it affect you?
- Overusing meta keywords can invite a Google penalty.
- Meta descriptions help increase your CTR (click-through rate). Google puts a default description for you (if you don’t), but it might not be too coherent or relevant to your purpose.
- Title tags are an essential factor for your search engine ranking. Titles not optimized with the right keywords won’t provide the needed context of your page to search engines and users.
- Robots help in indicating Noindex content. It appropriately indexes your content and displays it to the right audience. Not using this properly might invite google penalties for duplicate, irrelevant content, etc.
- Improper use of meta tags can adversely affect your SERPs, traffic, engagement rate, CTR, ranking, etc.
10. Not Following Google Webmaster Guidelines
Google helps you in your SEO efforts with various tools, one of which is webmaster tools. It gives you a lot of information about your website and offers various tools to improve your ranking and SEO efforts.
For instance, you can locate issues like crawling errors, duplicate content, poor links, etc.
How not following the guidelines can harm you?
- To rank well, Google asks you to keep your URLs simple, accurate, readable, and relevant. Bad URLs can adversely affect user experience, linking, crawling by Google, and your website’s rankings.
- It is suggested to keep your content unique. Duplicate content on your website can lead to losing traffic and rankings.
- Search engines ask you to make your links crawlable. If your pages are not crawlable, even without knowing, your page won’t show in the result pages, and you won’t be able to rank high on google.
Key Takeaways
- Don’t build links by sending mass requests, injecting through hacking, guest blogging, etc.
- Make sure your content isn’t plagiarized.
- Refrain from clickbait keywords
- Avoid using headlines that mislead the content of the article.
- Don’t write for robots (your audience is humans), and don’t get robots to write for you (generated content).
- Be mindful of technical errors and broken links.
- Don’t try tactics like article spinning, cloaking, etc.
- Avoid overusing anchor texts.
- Don’t create web pages for all keyword variations.
- Be mindful of targeting exact-match domain names or search queries.
- Don’t go for multiple proxy servers.
- Avoid using the generic file name for your images in the blog post.
Always approach SEO with the highest regards to the fact that it never gets completely done. We offer SEO services for businesses of all sizes, contact us today to see how we can help improve your ranking!